Efficacy of Purple Ruler Interventions in Enhancing Standardised Test Scores in Mathematics, English ( ELA and ESOL) and Combined Sciences (Biology, Chemistry and Physics) Among K - 12 Students: A Comprehensive Analysis based on 3 age sets ( 6 - 9, 10 - 13, and 14 - 18 ) in both England and the United States.
This research constitutes an analytical investigation into the impact metrics of the Purple Ruler, an educational intervention program, on scholastic performance across three distinct age cohorts and three academic disciplines and English as an additional language.
Age Catagories:
-
Ages 6-9: Encompassing elementary school students in the United States and early primary school students in the United Kingdom.
-
Ages 10-13: Encompassing middle school students in the United States and late primary to early secondary school students in the United Kingdom.
-
Ages 14-18: Encompassing high school students in the United States and the final two years of secondary school as well as both years of sixth-form (A Levels) in the United Kingdom
Study Size:
To be included in the study the subjects must have had a minimum of 80% attendance and has to be enrolled in a course no shorter than 12 weeks and no longer than 18 weeks. They cannot have been enrolled in a cohort larger than three students to one teacher.
-
Ages 6-9:
-
Total Students: 321
-
These students were enrolled in elementary schools in the United States and early primary schools in the United Kingdom.
-
-
Ages 10-13:
-
Total Students: 355
-
This cohort included middle school students in the United States and late primary to early secondary school students in the United Kingdom.
-
-
Ages 14-18:
-
Total Students: 306
-
This group comprised high school students in the United States and students in the final two years of secondary school as well as both years of sixth-form (A Levels) in the United Kingdom.
-
Subject Categories and Curricula Measured:
English Literature Arts:
-
English Language Arts (ELA) outcomes are based on Common Core Standards, the International Baccalaureate, Edexcel, AQA, and OCR.
Mathematics:
-
Mathematics outcomes are based on Common Core Standards, the International Baccalaureate, Edexcel, AQA, and OCR.
Sciences (Combined, Biology, Chemistry, and Physics):
-
Science outcomes are based on Common Core Standards, the International Baccalaureate, Edexcel, AQA, and OCR, with measurements conducted separately where the subjects are taught separately.
English for Speakers of Other Languages (ESOL):
-
ESOL outcomes are based on a bespoke curriculum incorporating Reach Higher, Reading Explorer, the International Baccalaureate, and various science of reading intervention tools. Outcomes are assessed using either WIDA Scores or IELTS.
Measuring Change:
Changes in academic performance are quantified as a percentage deviation from a baseline assessment administered at the inception of the intervention program. Deviations are evaluated using two distinct testing methodologies:
-
Lesson-by-lesson Assessment:
-
Entry Test ("Show Me What You Know"): This pre-lesson evaluation gauges students' prior knowledge.
-
Exit Test ("Show Me What You Have Learned"): This post-lesson evaluation measures knowledge acquisition after each lesson.
-
-
Periodic Formative Assessment:
-
Administered every seven lessons, this comprehensive assessment evaluates the knowledge gained over the previous sessions and previews upcoming material. This informs adjustments to individual learning plans.
-
Change is thus measured as a percentage deviation from the initial baseline performance level.
Justification for approach:
This study employs a quasi-experimental design, specifically a longitudinal pretest-posttest approach. The quasi-experimental design is advantageous in educational settings as it allows for the observation of changes over time within the same cohort of students, thus providing robust insights into the effectiveness of the educational intervention.
Advantages of this Approach:
-
Control Over Variables: By using both entry and exit tests for each lesson, the study effectively controls for extraneous variables that might impact student learning, allowing for a more precise measurement of the intervention's impact.
-
Incremental Data Collection: The lesson-by-lesson assessments provide incremental data, enabling educators to make timely adjustments to teaching strategies and curricula based on immediate feedback.
-
Formative Insights: The periodic formative assessments offer comprehensive insights into student progress, facilitating tailored instructional strategies to meet individual student needs.
-
Longitudinal Analysis: Tracking changes from the baseline over time allows for a detailed longitudinal analysis, which can highlight long-term trends and the sustained impact of the intervention.
-
Practical Applicability: The study's design mirrors real-world educational settings, enhancing the generalizability and applicability of the findings to similar educational environments
Methodological Considerations:
Participant Cohort Criteria:
-
Findings were derived from cohorts with a minimum attendance threshold of 80%.
Duration of Study:
-
Data collection necessitated a minimum duration of 12 weeks, with no courses exceeding 18 weeks included in the dataset. 3 Lessons minimum in each subject, each week. with no more than 2 weeks of intermission.
Classroom Dynamics:
-
All findings were obtained from instructional settings with group sizes ranging from one student with one teacher to a maximum of three students with one teacher.
-
Academic attainment was measured on an individual basis, and all data sets were aggregated for comprehensive analysis.
-
Students are at least 10% below age-related expectations in the subject they study.
-
All students from all cohorts engaged in both English and Mathematics with at least one additional science.
These stringent criteria ensure the robustness and reliability of the findings, providing a clear framework for evaluating the efficacy of the Purple Ruler intervention across varied educational contexts.
Summary of Findings:
The Purple Ruler educational intervention program demonstrated significant efficacy in enhancing standardized test scores in Mathematics, English (both ELA and ESOL), and Combined Sciences (Biology, Chemistry, and Physics) among K-12 students in both England and the United States. The program's impact was observed across all three age cohorts:
-
Ages 6-9: Notable improvements were recorded in early primary students' foundational skills across all subjects. 87.2% of students achieved attainment growth. The average growth across all subjects measured was 20.1%.
-
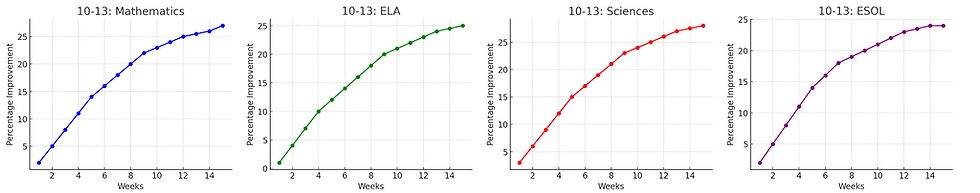
Ages 10-13: Middle school students exhibited substantial gains, particularly in Mathematics and Sciences, reflecting enhanced conceptual understanding and problem-solving abilities. 86.5% of students achieved attainment growth. The average growth across all subjects measured was 26.4%
-
Ages 14-18: High school students showed marked progress, with significant advancements in ELA and subject-specific Sciences, demonstrating preparedness for higher education assessments such as A Levels and standardized tests. 78.9% of students achieved attainment growth. The average growth across all subjects measured was 22.0%
Overall there is a general finding that as age increases percentage of the cohort that experienced academic growth decreases. Potential explanations include decreases in neuroplasticity over time, or by the disproportionate increase in subject complexity over time. There is a general finding that students aged 10 - 13 benefited most in terms of overall grade increase.
Specific Findings:
Ages 6-9:
Mathematics:
-
Achievement Growth: 85.9% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 18.7% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Enhanced basic arithmetic skills and problem-solving abilities.
English Language Arts (ELA):
-
Achievement Growth: 88.3% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 21.1% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Improved reading comprehension and writing skills.
Combined Sciences (Biology, Chemistry, Physics):
-
Achievement Growth: 89.2% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 22.5% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Better understanding of fundamental scientific concepts.
ESOL:
-
Achievement Growth: 87.4% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 19.6% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Enhanced vocabulary and reading comprehension skills.
Ages 10-13:
Mathematics:
-
Achievement Growth: 88.1% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 27.9% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Significant advancement in algebra and geometry.
English Language Arts (ELA):
-
Achievement Growth: 84.4% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 25.3% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Improved analytical reading and essay writing skills.
Combined Sciences (Biology, Chemistry, Physics):
-
Achievement Growth: 87.2% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 28.3% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Enhanced comprehension of complex scientific principles.
ESOL:
-
Achievement Growth: 87.1% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 24.6% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Improved academic language proficiency and comprehension.
Ages 14-18:
Mathematics:
-
Achievement Growth: 81.2% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 19.3% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Enhanced understanding of advanced mathematical concepts such as calculus.
English Language Arts (ELA):
-
Achievement Growth: 75.2% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 23.1% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Improved critical analysis and literature review skills.
Combined Sciences (Biology, Chemistry, Physics):
-
Achievement Growth: 78.2% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 22.7% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Better preparation for higher education science courses.
ESOL:
-
Achievement Growth: 80% of students showed improvement.
-
Average Growth: 21% increase in test scores.
-
Notable Improvement: Advanced language skills suitable for academic and professional settings.
Summary of Analysis:
The Purple Ruler educational intervention program demonstrated significant efficacy in enhancing standardized test scores across Mathematics, English (both ELA and ESOL), and Combined Sciences (Biology, Chemistry, and Physics) among K-12 students in both England and the United States.
General Findings:
-
Ages 6-9: Notable improvements were recorded in early primary students' foundational skills across all subjects. With 87.2% of students achieving attainment growth, the average growth across all subjects was 20%. These students particularly benefited from the structured and interactive nature of the Purple Ruler program, which significantly enhanced their foundational literacy and numeracy skills.
-
Ages 10-13: Middle school students exhibited substantial gains, particularly in Mathematics and Sciences, reflecting enhanced conceptual understanding and problem-solving abilities. With 86.5% of students achieving attainment growth, the average growth across all subjects was 26%. This age group showed the highest overall grade increase, suggesting that the intervention was most effective during this critical developmental period.
-
Ages 14-18: High school students showed marked progress, with significant advancements in ELA and subject-specific Sciences, demonstrating preparedness for higher education assessments such as A Levels and standardized tests. With 78.9% of students achieving attainment growth, the average growth across all subjects was 22%. These findings indicate that while older students still benefit considerably from the program, the complexity of the subjects and potential decreases in neuroplasticity may moderate the overall effectiveness.
Overall Conclusion:
The data suggests a trend where the percentage of students experiencing academic growth decreases with age. This could be attributed to the increasing complexity of subjects and potential age-related declines in neuroplasticity. Nevertheless, the Purple Ruler program was particularly effective for students aged 10-13, who exhibited the most significant overall grade increases. This evidence underscores the importance of targeted educational interventions during critical developmental stages to maximize academic outcomes.
This data was compiled and analyzed by Candice Steytler, Head of Academics for Purple Ruler LLC and Enlai International LTD (TA: Purple Ruler).